Lipid composition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and its relevance for particle formation, stability and infectivity
Principal investigator: Kräusslich
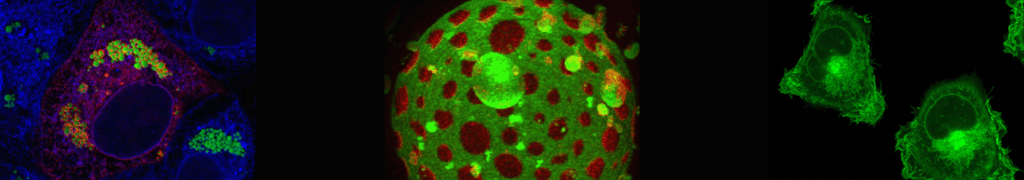
The viral Gag polyprotein is recruited to the plasma membrane (PM) in a PI(4,5)P2 dependent manner and appears to induce a membrane microdomain highly enriched in putative raft lipids that serves as budding platform and recruits glycoproteins and other components as e.g. tetraspanins. We found that PM PI(4,5)P2 is not only essential for membrane recruitment of HIV-1 Gag, but also to maintain the assembled Gag lattice at the PM. Using lipidomics and lipid-protein cross-linking approaches as well as live-cell and super-resolution imaging of proteins and lipids at viral assembly sites, we will continue and extend our studies of protein-lipid interactions at HIV-1 assembly sites to determine mechanism and function of virus-specific microdomain formation.